
Stages of Startups
Startups are often seen as innovative and promising ventures that have the potential to disrupt industries and bring new solutions to the market. However, understanding the different stages of a startup is crucial for its success. In this blog post, we will explore the definition of a startup, the importance of comprehending its various stages, and a brief history and evolution of the concept.
A startup is a young company that is in the initial stages of its operation. It is characterized by its focus on developing and scaling a unique product or service that has the potential to meet a market need. Startups are driven by innovation, agility, and a desire to overgrow.

Comprehending the different stages of a startup is essential for entrepreneurs and investors alike. Each stage comes with its challenges, opportunities, and requirements. By understanding these stages, founders can better navigate their startup's growth trajectory, make informed decisions, and secure necessary resources. On the other hand, investors can evaluate startups based on their stage and align their investment strategies accordingly.
Brief History and Evolution of the Concept
The concept of startups gained prominence in the late 20th century with the rise of technology and internet-related companies. Silicon Valley became a hub for startups, and success stories like Apple and Microsoft fueled the interest in this type of venture. Over time, the startup ecosystem has evolved, with the emergence of incubators, accelerators, and angel investors who provide support and resources to early-stage startups.
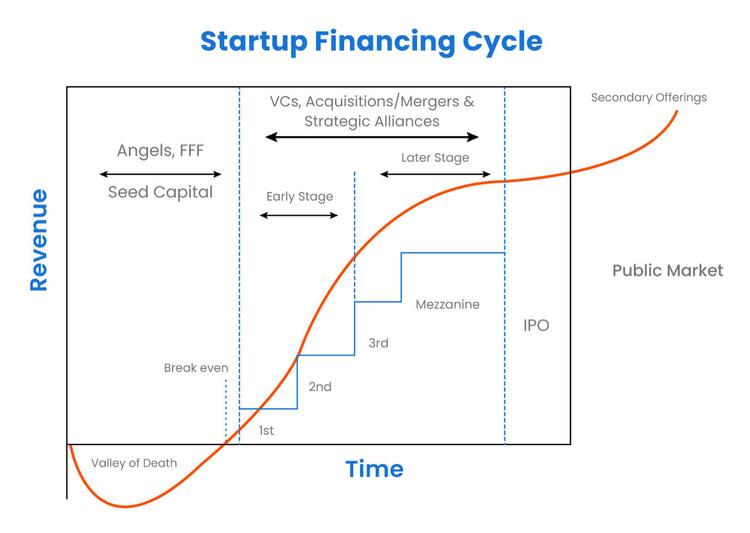
Stage 1: Ideation and Pre-Seed:
This stage involves generating and evaluating ideas, assessing their feasibility, and developing a basic business model. Founders seek potential cofounders and form an initial team. Personal resources and self-funding are often used to finance the startup's initial operations.
Stage 2: Seed:
During this stage, early-stage investors are sought to provide funding for further development. The startup focuses on building a minimum viable product (MVP) and validating the market through user feedback. It also formulates an early growth strategy while managing limited financial resources.
Stage 3: Series A:
The startup raises significant funding from venture capitalists to scale its operations. The team expands, roles become more specialized, and the product and business model undergo refinement. Marketing, sales, and branding efforts intensify as the startup aims to gain a larger market share.
Future Stages:
Beyond Series A, startups may go through additional funding rounds such as Series B, C, and beyond. These stages involve securing more substantial investments to support continued growth, expand into new markets, and achieve profitability.
Understanding the different stages of a startup is crucial for entrepreneurs and investors alike. By being aware of the challenges and opportunities at each stage, founders can navigate their startup's growth effectively. Investors can align their investment strategies with the startup's stage, increasing the likelihood of a mutually beneficial partnership.

